What is CAPA in the Pharmaceutical Industry?

CAPA is Corrective and Preventive Action, holds immense significance in the pharmaceutical industry. The purpose of CAPA is to identify, analyze, and address problems by taking corrective actions and implementing preventive measures to mitigate the chances of recurrence.
In the pharmaceutical sector, where the effects of medications can profoundly impact individuals’ health and well-being, having robust CAPA capabilities integrated into a Quality Management System (QMS) is crucial.
The upcoming blog is aimed at providing comprehensive details about CAPA, with a specific focus on its role within the pharmaceutical industry. It will cover various aspects related to CAPA, including its definition, importance, processes, and implementation in pharmaceutical settings.
The blog aims to delve deep into how pharmaceutical industries can utilize CAPA effectively to ensure the safety, quality, and reliability of their products.
Table of content:
- What is CAPA?
- When CAPA is triggered?
- Sources of CAPA
- Importance of CAPA in pharmaceutical industry
- Steps for CAPA in pharmaceutical industry
- Conclusion
What is CAPA (Corrective Action Preventive Action)?
Corrective Action Preventive Action (CAPA) is a systematic approach used to address anomalies or inconsistencies within processes to prevent their recurrence. It’s an established system designed to ensure adherence to quality standards and regulatory requirements.
When CAPA is triggered?
As CAPA mitigates occurrence of deviations, it is triggered on encounter of a deviation. But every deviation does not trigger CAPA.
CAPA is a time taking and cost involving process, hence minor nonconformances (NCs), or deviations do not require a CAPA to trigger.
For example – If a capsule is leaked and liquid comes out of it, such severe deviations trigger CAPA.
Another example could be of having broken/ open seal of a syrup bottle. Deviations like these trigger CAPA.
Example where NC will not trigger CAPA – In a pharmaceutical organization, a batch of finished pharmaceutical products has labels that are slightly misaligned, but all essential information, including the drug name, strength, and expiration date, is accurate.
Such NC will not trigger a CAPA, since it is not a major issue. This can be rectified without procedural trails from the next batch.
Sources of CAPA:
A pharma industry can have various sources of CAPA, such as:
Non-conformance –
Non-conformance is deviation from standard process or product. Non- conformance is also inability to meet the standards – standard of quality or process or procedure. An NC, if neglected, eventually will lower customer satisfaction.
For example – A capsule is supposed to be packed in double layer packaging material. QC reported that the packaging of the capsule has been a single layer packaging. This is a nonconformance in process. Hence, a CAPA triggered will have nonconformance source.
Customer complaint – When customer of a product raises complaint against a product. The CAPA raised will have source customer complaint.
For example- a patient orders paracetamol, and the company delivers anti allergic tablet, the CAPA triggered will have customer complaint as source.
Audit finding –
When the existing quality system is found unaligned with established quality system of the company, it triggers a CAPA sourced from audit.
Any good and robust pharma QMS software, like QualityPro, allows to define source of CAPA. Along with defining source of CAPA, QualityPro also allows to attach various relevant documents. This additional document helps to understand the issue, find out the cause of the issue and plan for remedies faster.
Importance of CAPA in Pharmaceutical Industry:
Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA) are of utmost importance in the pharmaceutical industry for several reasons:
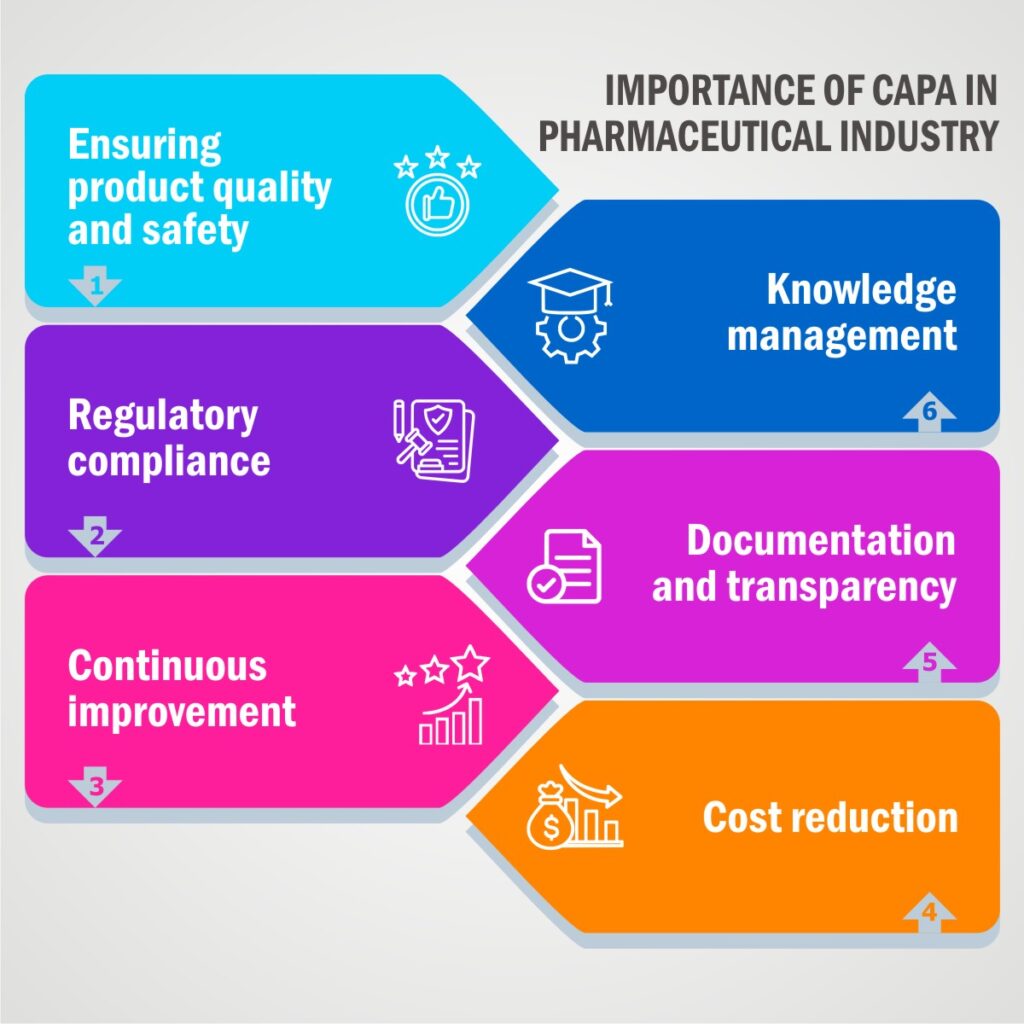
Ensuring Product Quality and Safety:
The primary goal of pharmaceutical CAPA is to maintain and enhance product quality and safety. CAPA processes help identify and address deviations, non-conformities, and quality issues promptly, reducing the risk of substandard or unsafe products reaching consumers.
Regulatory Compliance:
Regulatory bodies such as the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) and EMA (European Medicines Agency) have stringent requirements for pharmaceutical companies. CAPA is crucial for compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other regulations. Non-compliance can lead to regulatory actions, recalls, and legal consequences.
Continuous Improvement:
Pharma CAPA fosters a culture of continuous improvement within pharmaceutical companies. By investigating and addressing root causes of problems, CAPA helps organizations identify opportunities for process improvement and efficiency gains.
Cost Reduction:
Identifying and addressing issues early through CAPA can reduce the overall cost of quality in pharmaceutical manufacturing. It helps prevent costly recalls, rework, and regulatory fines.
Documentation and Transparency:
CAPA in pharma requires thorough documentation of investigations, actions taken, and outcomes. This documentation provides transparency to regulatory agencies and auditors, demonstrating the company’s commitment to quality and compliance.
Knowledge Management:
CAPA investigations can give valuable insights and lessons regarding current and future product development and manufacturing processes. Knowledge gained through CAPA can be used to improve product designs and prevent similar issues in the future.
Steps for CAPA in Pharmaceutical Industry:
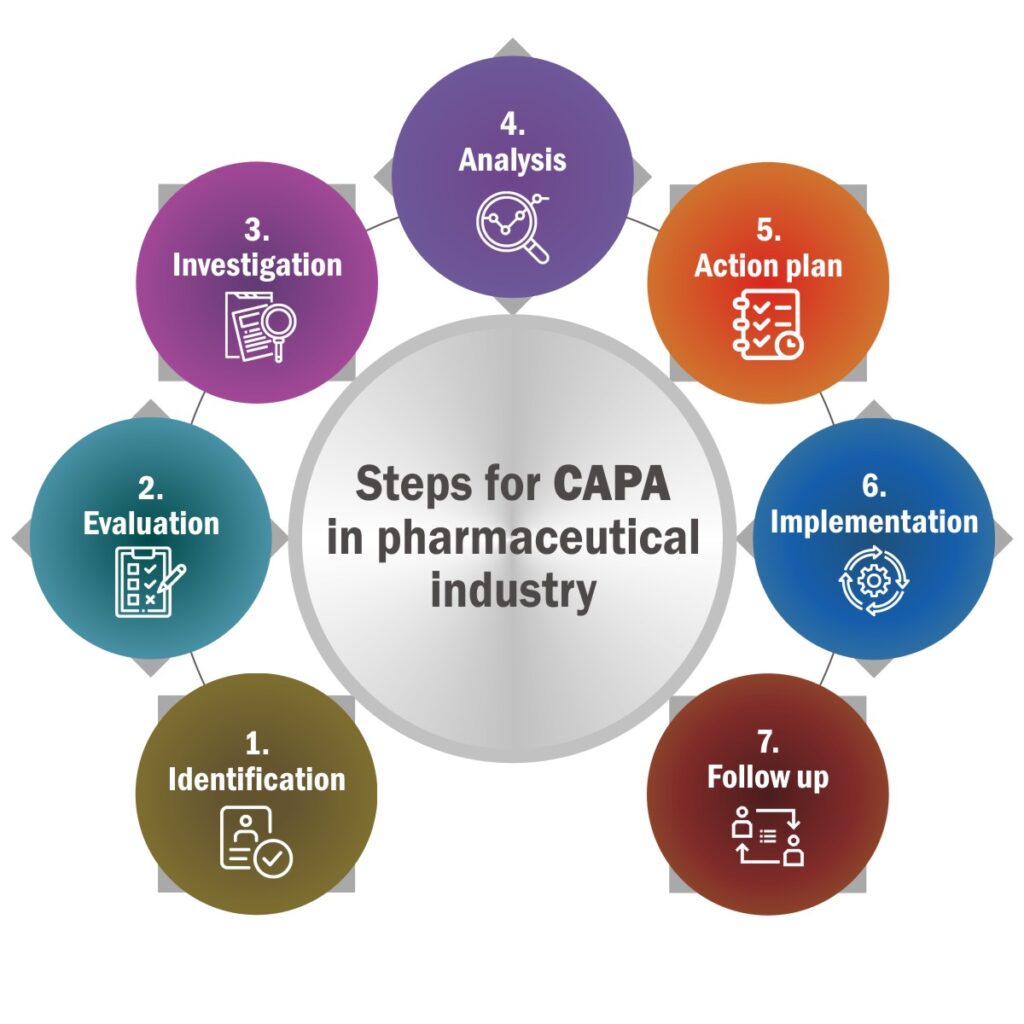
Identification – CAPA starts with identification. It requires identification of all the issues that require CAPA. It also records source of the issues.
Evaluation – After identification it’s time to evaluate to decide if the issue requires CAPA or not.
Investigation – This step is necessary to identify root cause of the issue. Investigation includes issue identification, documentation, formation of an investigation team.
Analysis – The next step is to analyse root cause of the issue. It involves documenting data, analyse it, and find inferences for action plan.
Action plan – Make a plan which is feasible for organization to implement. The effectiveness of this step largely depends upon the correctness of previous step.
Implementation – It is about implementing the action plan decided in previous step. It requires documentation of implementation of plan, its desired output, steps, and observation.
Follow up – Once the plan is implemented, follow up will help to records and measures the effectiveness of the plan implemented.
Conclusion:
Pharma industry is very sensitive. Even a minor error and deviation in result from standard can trigger nasty repercussions. Consumers can sue the organization and regulatory organizations can put heavy penalties against the organization.
Besides monetary loss, the organizations can suffer trust depletion. In pharmaceutical sector trust is the paramount factor for any organization.
Once found erroneous, such pharma organization will struggle to gain business momentum in the market. Hence, they need to be full proof.
In such a fierce market, paper based CAPA management process is a perfect formula for errors and disaster. Having a paper based CAPA management process and Pharma QMS is as good as having no system at all.
Organizations must seek digital solutions to manage CAPA effectively. Also, to ensure quality culture in the organization, it must have a digital QMS in place.
Besides, being error prone, paper-based processes is location dependent. In the fast-paced market like today’s, organizations need a solution which is quick, fast, and anytime anywhere available.
QualityPro is one such solution for all such challenges. It is a cloud based QMS solution which digitizes and automates processes and documentation. It has a full proof CAPA management capability to check all the boxes of quality culture and compliance requisites.
With more than 2000 customers world-wide, QualityPro is an ace of spades. To know more about it, please mail us on contact@bmqualitymaster.com.




