What is the Difference between Quality Control and Quality Assurance?

What do you make of the terms Quality Assurance and Quality Control? Are they two sides of the same coin, or do we unnecessarily mix them up? And if they indeed are different, what points do they differ on, and why is it important to know about those differences? Let’s find out.
Overview
It goes without saying that the most important objective for every organization has to be designing and delivering products as well as services of the highest quality. To help achieve this goal, quality management plays an extremely crucial role. Also Read: Difference between Quality Management and Quality Control
Quality Control (QC) and Quality Assurance (QA), the two focus areas of this blog, constitute an integral part of quality management. And hence, it becomes essential for every stakeholder to understand what QC and QA are, what their intricacies are, and how the two are different.
It is particularly important to understand the concepts of Quality Control and Quality Assurance, because there is a lot of ambiguity around the two terms, with quite a few people using them interchangeably. Even though the two are aspects of quality management, they are different in their focus. Also Read: What is the difference between Project management and Quality Management?
Through this blog, let’s understand what their definitions are, before proceeding to see the differences between them.
What is Quality Assurance?
The ISO (International Standardization Organization) defines Quality Assurance as, “Part of quality management focused on providing confidence that quality requirements will be fulfilled.”
Quality Assurance can be defined as a set of activities that are performed to ensure quality in the processes by which organizations develop their products or services in such a way that they satisfy the customer expectations.
Quality Assurance focuses on preventing defects, apart from planning, documenting, and implementing guidelines essential to assure quality output. It also includes monitoring and verifying whether the due processes have been followed, or not.
What is Quality Control?
ISO 9000 describes Quality Control as, “part of quality management focused on fulfilling quality requirements.”
Another crucial component of quality management, Quality Control can be defined as a set of activities that are performed to ensure the quality of the products or services that have been delivered.
That way, it is a strategy that’s being executed when the product has passed the development stage, and has entered into the manufacturing stage. It includes all the activities that are designed to determine the level of quality of delivered products and services.
Being reactive in nature, Quality Control focuses on identifying the defects, and can be performed only after Quality Assurance has been done. It also includes monitoring and verifying whether the project deliverables met the desired quality standards or not.
How are the two different?
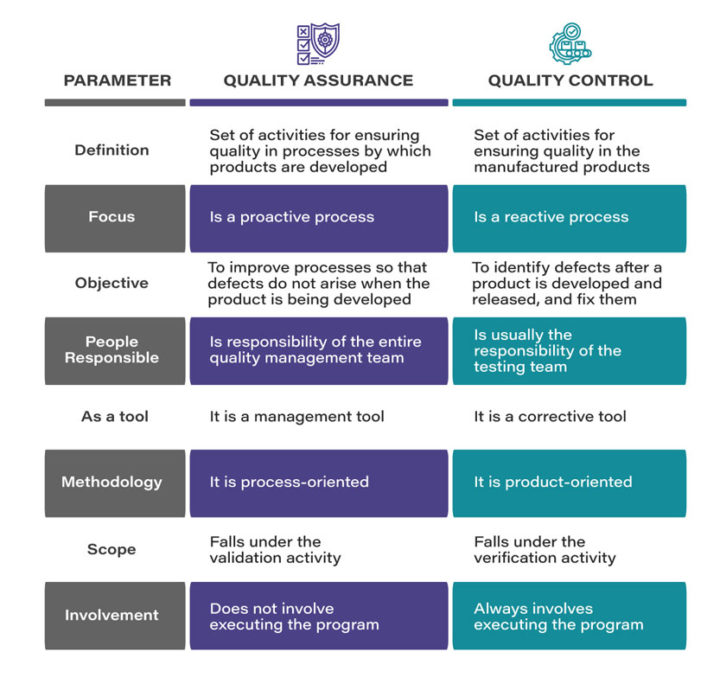
Focus: An important point the two approaches differ on happens to be the focus. Quality Assurance — being proactive in nature — focuses on preventing the defects before they occur, and also on steps to design processes like documenting standard operating procedures (SOPs). It ensures that the processes are followed effectively so that safe products of desired quality are delivered.
On the other hand, Quality Control, which is reactive in nature, identifies defects once they occur. It also ensures that the processes are duly followed to deliver products of highest quality, besides testing the products post production to check whether all the safety measures are met or not.
Orientation: Another point where Quality Assurance and Quality Control differ is their orientation. Quality Assurance is essentially process-oriented. It focuses on preventing quality issues, with an emphasis on designing processes such as documentations, audits, training, change management, etc. in such way that any defects are avoided.
Quality Control, on the other hand, is product-oriented. As mentioned earlier, it identifies the quality issues in the products that have already been manufactured. So where the two approaches essentially differ is the fact that while QA involves the processes that create the product, QC focuses on the finished product through processes such as batch monitoring, inspection, validation, and testing, etc.
Responsibility: Lastly, responsibility is another point where the two differ from each other. The Quality Assurance activities are predominantly the responsibility of the entire quality management team. Every single team member is responsible for ensuring that the SOPs are being followed, and contributing towards designing the quality procedures.
Quality Control, on the other hand, happens to be the responsibility of the testing team within the quality management team, which is supposed to follow the SOPs. The QC team is also supposed to document the results of product testing based on the standard procedures for product validation.
To sum up
Both Quality Assurance and Quality Control constitute an integral part of the quality management process for any organization. Understanding the two concepts, and the differences between them in a better manner, will help the quality management professionals to design, assess, and execute their plans efficiently so as to ensure the final output is of highest quality.
A Quality management software such as QualityMaster covers both the quality assurance as well as control aspects, while handling the broader concept of quality management. Want to know how this quality control system can help you manage Quality Assurance and Quality Control processes in particular, and quality in general? Get in touch for a free demo of this best-in-class QMS software.